Gespeicherte und gekühlte Ionen
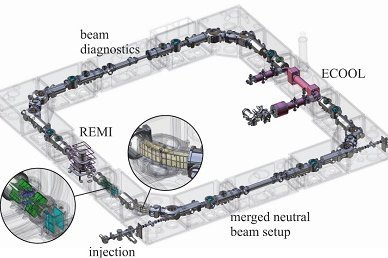
Die experimentelle Abteilung „Gespeicherte und gekühlte Ionen“ befasst sich mit Präzisionsexperimenten zur Bestimmung von atomaren und nuklearen Grundzustandseigenschaften gespeicherter Ionen für Tests fundamentaler Wechselwirkungen und ihren Symmetrien sowie mit der Erforschung elementarer Prozesse molekularer Ionen. Dazu werden kurzlebige Radionuklide, Antimaterie, hochgeladene Ionen oder einfache Molekülionen in Penningfallen oder im kryogenen Speicherring CSR unter Weltraumbedingungen gefangen. Auch die Entwicklung neuer Speicher-, Kühl- und Nachweistechniken für zukünftige Experimente ist ein wichtiger Forschungsschwerpunkt der Abteilung.
Nachrichten
Mit vereinten Kräften auf der Suche nach neuer Physik
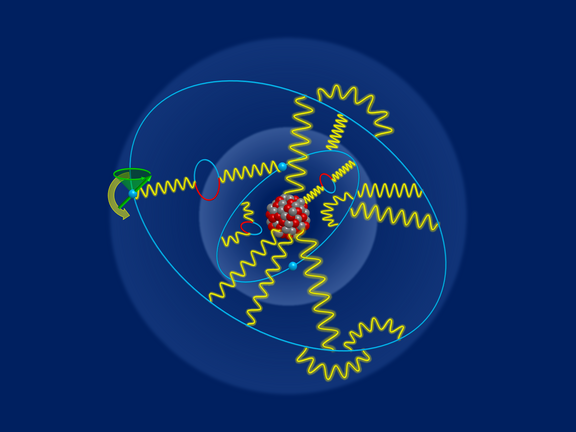
In internationaler Zusammenarbeit mit anderen Instituten haben MPIK-Forschende hochpräzise Messungen und Berechnungen zu atomaren Übergängen in…
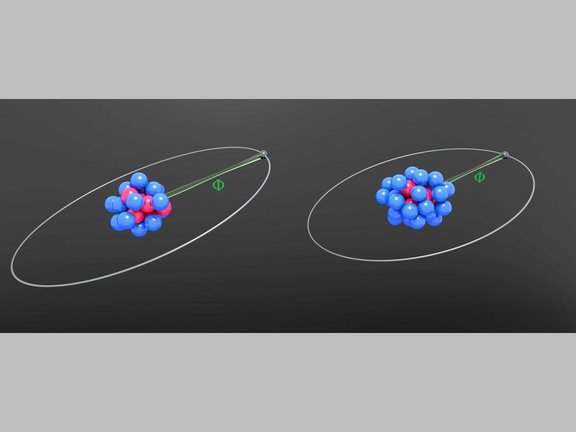
Elektronen im Gespräch belauscht: Messung des g-Faktors von lithiumhaltigem Zinn
Forschende des MPIK präsentieren neue experimentelle und theoretische Ergebnisse für den g-Faktor von gebundenen Elektronen in lithiumähnlichem Zinn,…