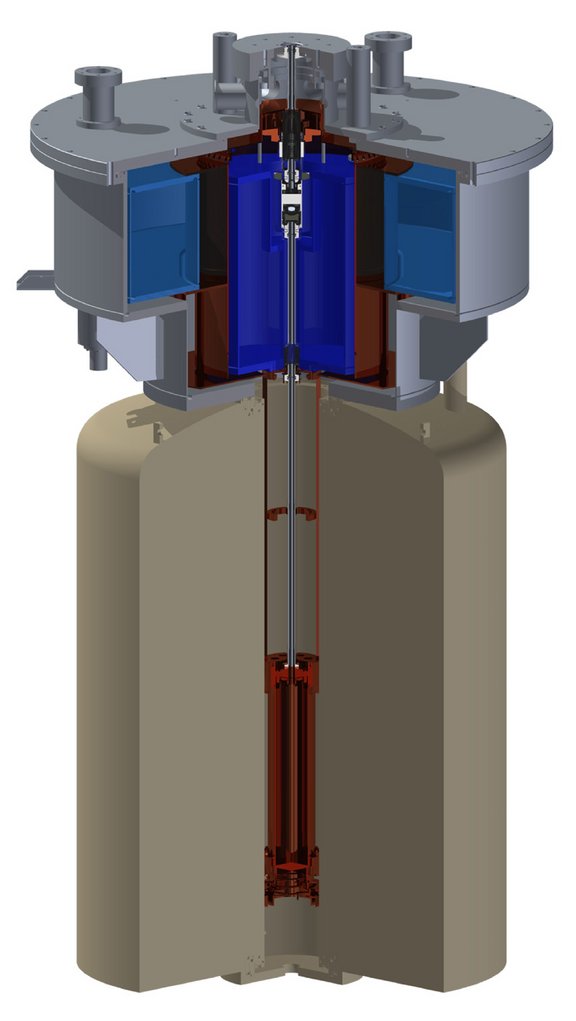
ALPHATRAP
Zur Messung des g-Faktors des Elektrons in extrem schweren Ionen wird derzeit am MPIK eine neue kryogene Penningfalle namens ALPHATRAP entwickelt. Für die Falle besteht Zugang zur Heidelberg EBIT [1], welche extrem schwere hochgeladene Ionen bis zu 208Pb81+ liefern kann. Mit solchen Systemen ist es möglich die QED in extremen Feldstärken an der Grenze unseres Wissens zu testen. Die Ionen werden über eine Beamline mit Ionenoptikelementen und Diagnoseeinheiten zu ALPHATRAP transportiert. Die Falle ist in einem Flüssigheliumkryostaten angebracht, um eine kryogene Umgebung bereitzustellen. Um geeignete Hochvakuumbedingungen zur Speicherung von hochgeladenen Ionen sicherzustellen, wurde ein kryogenes Vakuumventil entwickelt um die Beamline mit Raumtemperaturvakuum von der Fallenregion zu trennen.
Außer den mechanischen Unterschieden durch den offenen Aufbau können die meisten technischen Elemente prinzipiell aus dem Mainzer Aufbau übernommen werden. Es sind jedoch Anpassungen aus verschiedenen Gründen nötig. Beispielsweise führen die hohen Ladungszustände zu einer systematischen Verschiebung der Ionenfrequenzen aufgrund eines Spiegelladungseffektes. Dadurch wird ein im Vergleich zur Mainzer Falle größerer Falleninnenradius zwingend nötig. Ein weiteres Beispiel ist ein noch komplexeres und anspruchsvolleres Detektionssystem, welches im Moment entwickelt wird.
Referenzen
| [1] | Optimization of the charge state distribution of the ion beam extracted from an EBIT by dielectronic recombination |
| J. R. Crespo López-Urrutia, J. Braun1, G. Brenner, H. Bruhns, A. Lapierre, A. J. González Martı́nez, V. Mironov, R. Soria Orts, H. Tawara, M. Trinczek and J. Ullrich | |
| Rev. Sci. Instrum. 75, 1560 (2004) |
ERC Advanced Grant
This project receives funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 832848 - FunI.
12Testing interelectronic interaction in lithium-like tin
J. Morgner, V. A. Yerokhin, C. König, F. Heiße, B. Tu, T. Sailer, B. Sikora, Z. Harman, J. R. Crespo Lopez-Urrutia, C. H. Keitel, S. Sturm, and K. Blaum
Science 388, 6750, 945-949 (2025)
MPIK press release: Listening to electrons talk: g-factor measurement of lithium-like tin
MPIK-Pressemitteilung: Elektronen im Gespräch belauscht: Messung des g-Faktors von lithiumhaltigem Zinn
Phys.org: Listening to electrons 'talk': Lithium-like tin's g-factor measured with 0.5 parts per billion experimental accuracy
ScienceDaily: Listening to electrons talk: g-factor measurement of lithium-like tin
idw-Pressemitteilung: Elektronen im Gespräch belauscht: Messung des g-Faktors von lithiumhaltigem Zinn
11Nondestructive Control of the Rovibrational Ground State of a Single Molecular Hydrogen Ion in a Penning Trap
C. M. König, F. Heiße, J. Morgner, T. Sailer, B. Tu, D. Bakalov, K. Blaum, S. Schiller, and S. Sturm
Physical Review Letters 134, 163001 (2025)
10g Factor of Boronlike Tin
J. Morgner, B. Tu, M. Moretti, C. M. König., F. Heiße, T. Sailer, V. A. Yerokhin, B. Sikora, N. S. Oreshkina, Z. Harman, C. H. Keitel, S. Sturm, and K. Blaum
Physical Review Letters 134, 123201 (2025)
Phys. Rev. Lett.: Editors' Suggestion
MPIK press release: A new benchmark for quantum electrodynamics in atoms
MPIK-Pressemitteilung: Ein neuer Bezugswert für Quantenelektrodynamik in Atomen
Phys.org: A new benchmark for quantum electrodynamics in atoms: Precision measurement of boron-like tin ion's g factor
idw-Pressemitteilung: Ein neuer Bezugswert für die Quantenelektrodynamik in Atomen
9High-Precision Determination of g Factors and Masses of 20Ne9+ and 22Ne9+
F. Heiße, M. Door, T. Sailer, P. Filianin, J. Herkenhoff, C. M. König., K. Kromer, D. Lange, J. Morgner, A. Rischka, C.. Schweiger, B. Tu, Y. N. Novikov, S. Eliseev, S. Sturm, and K. Blaum
Physical Review Letters 131, 253002 (2023)
8Stringent test of QED with hydrogen-like tin
J. Morgner, B. Tu, C. M. König., T. Sailer, F. Heiße, H. Bekker, B. Sikora, C. Lyu, V. A. Yerokhin, Z. Harman, J. R. Crespo López-Urrutia, C. H. Keitel, S. Sturm, and K. Blaum
Nature 622, 53-57 (2023)
MPIK press release: Precise testing of quantum electrodynamics
MPIK-Pressemitteilung: Quantenelektrodynamik auf dem Prüfstand
MPG press release: When the laws of physics are at stake - Quantum electrodynamics put to the test
MPG-Presssemitteilung: Wenn Gesetze der Physik auf dem Spiel stehen - Quantenelektrodynamik auf dem Prüfstand
Nature research briefings: Testing the limits of the standard model of particle physics with a heavy, highly charged ion
phys.org: A precise test of quantum electrodynamics: Measuring the g factor of electrons in hydrogen-like tin
7Measurement of the bound-electron g-factor difference in coupled ions
T. Sailer, V. Debierre, Z. Harman, F. Heiße, C. König, J. Morgner, B. Tu, A. V. Volotka, C. H. Keitel, K. Blaum, and S. Sturm
Nature 606, 479-483 (2022)
Nature News & Views: Tiny isotopic difference tests standard model of particle physics
MPIK press release: Quantum electrodynamics tested 100 times more accurately
MPIK-Pressemitteilung: Quantenelektrodynamik 100-fach genauerer getestet
phys.org: Quantum electrodynamics tested 100 times more accurately than ever
pro-physik.de: Präzisionsprüfung der Quantenelektrodynamik
6Tank-Circuit Assisted Coupling Method for Sympathetic Laser Cooling
B. Tu, F. Hahne, I. Arapoglou, A. Egl, F. Heiße, M. Höcker, C. König, J. Morgner, T. Sailer, A. Weigel, R. Wolf, and S. Sturm
Advanced Quantum Technologies 4, 2100029 (2021)
5Perspectives on testing fundamental physics with highly charged ions in Penning traps
K. Blaum, S. Eliseev, and S. Sturm
Quantum Science and Technology 6, 014002 (2020)
4g Factor of Lithiumlike Silicon: New Challenge to Bound-State QED
D. A. Glazov, F. Köhler-Langes, A. V. Volotka, K. Blaum, F. Heiße, G. Plunien, W. Quint, S. Rau, V. M. Shabaev, S. Sturm, and G. Werth
Physical Review Letters 123, 173001 (2019)
3Application of the Continuous Stern-Gerlach Effect for Laser Spectroscopy of the 40Ar13+ Fine Structure in a Penning Trap
A. Egl, I. Arapoglou, M. Höcker, K. König, T. Ratajczyk, T. Sailer, B. Tu, A. Weigel, K. Blaum, W. Nörtershäuser, and S. Sturm
Physical Review Letters 123, 123001 (2019)
2g Factor of Boronlike Argon 40Ar13+
I. Arapoglou, A. Egl, M. Höcker, T. Sailer, B. Tu, A. Weigel, R. Wolf, H. Cakir, V. A. Yerokhin, N. S. Oreshkina, V. A. Agababaev, A. V. Volotka, D. V. Zinenko, D. A. Glazov, Z. Harman, C. H. Keitel, S. Sturm, and K. Blaum
Physical Review Letters 122, 253001 (2019)
pro-physik.de: Alphatrap-Experiment liefert erste Ergebnisse
idw press release: First results of the new Alphatrap experiment
MPIK-Pressemitteilung: Erste Resultate des neuen ALPHATRAP-Experiments
1The ALPHATRAP experiment
S. Sturm, I. Arapoglou, A. Egl, M. Höcker, S. Kraemer, T. Sailer, B. Tu, A. Weigel, R. Wolf, J. R. Crespo López-Urrutia, and K. Blaum
European Physical Journal - Special Topics 227, 1425-1491 (2019)